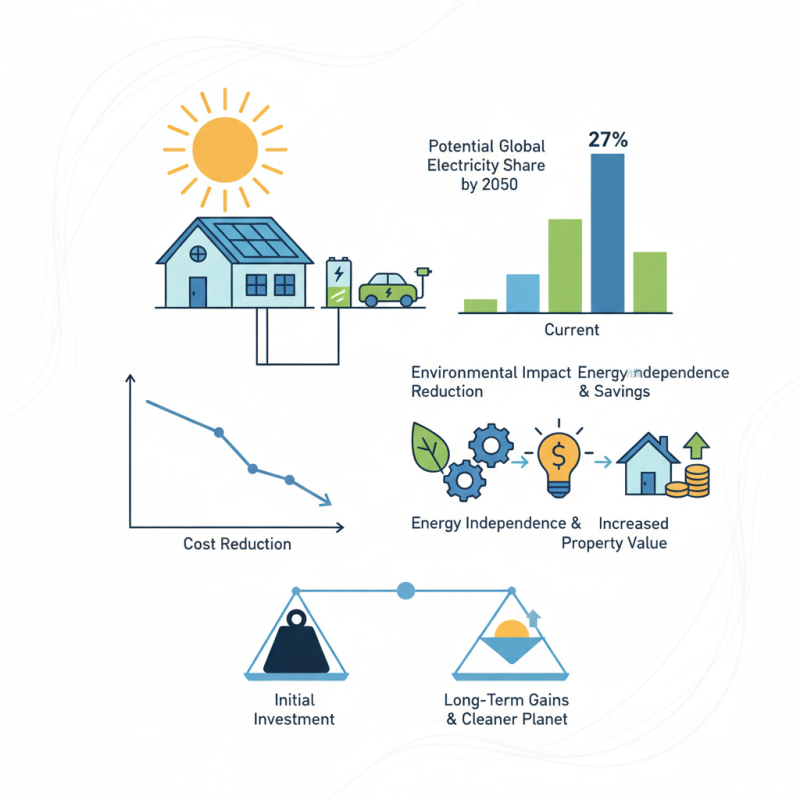
As the world grapples with climate change, a solar energy system emerges as a top contender for sustainable power. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar energy could provide up to 27% of global electricity by 2050. This significant potential reflects a shift toward greener solutions. A solar energy system not only reduces carbon emissions but also fosters energy independence.
Moreover, the cost of solar technology has plummeted. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory reports that solar panel prices have dropped by over 80% since 2010. This affordability makes solar energy accessible to many. However, challenges remain. Initial installation costs can still be a barrier for some homeowners and businesses. Many are also skeptical about efficiency and reliability.
Despite these concerns, the benefits are compelling. A solar energy system can significantly lower utility bills and increase property values. Transitioning to this technology can be a step toward a more sustainable future. Customers must weigh the initial investment against long-term gains. Doing so could ensure a cleaner planet for generations to come.
A solar energy system converts sunlight into usable electricity. It consists of solar panels, inverters, and batteries. These components work together to harness solar power. Solar panels are typically installed on rooftops or in open fields. They capture sunlight and generate direct current (DC) electricity.
The inverter then changes this DC electricity into alternating current (AC), which powers homes and businesses. Batteries are optional but useful for storing excess energy. This stored energy can be used when the sun isn’t shining. However, installation can be costly and requires space. Not every location is ideal for solar panels. Shade from trees or buildings can significantly reduce efficiency.
Moreover, the performance of a solar energy system depends on regional sunlight hours. In areas with less sunlight, the output may not meet energy needs. It’s important to consider local conditions carefully. For some, the decision to go solar may bring unexplored challenges. Balancing costs, efficiency, and environmental impact can be tricky. This complexity invites deeper reflection before making the switch.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Sustainability | Solar energy is renewable and reduces dependence on fossil fuels. |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly lowers carbon footprint and greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Cost Savings | Decreases electricity bills and has low maintenance costs. |
| Energy Independence | Reduces reliance on imported energy sources and enhances local energy production. |
| Job Creation | Growing solar energy sector leads to job opportunities in various fields. |
| Technology Advancement | Continuous innovations lead to more efficient solar panels and storage solutions. |
| Grid Stability | Distributed solar systems can enhance grid resilience against outages. |
Solar energy offers numerous benefits for sustainable power generation. According to the International Energy Agency, solar power accounted for 12% of global energy production in 2022, a significant increase from previous years. This surge indicates a growing transition towards cleaner energy sources. One of the most appealing aspects of solar energy is its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For every megawatt-hour of solar energy produced, approximately 0.5 tons of carbon dioxide could be avoided compared to fossil fuels.
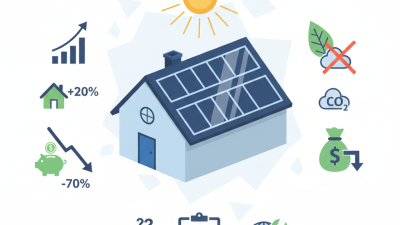
Adopting solar solutions can lead to substantial savings. Studies show that households with solar systems can save an average of $1,500 per year on energy costs. Additionally, the Environmental Protection Agency reported that transitioning to solar energy can prevent millions of tons of carbon emissions annually. However, the initial installation costs can be a barrier for many. Some people hesitate due to the upfront investment. This hesitation is understandable but worth reconsidering in the long run.
Solar power can increase energy independence for communities. By generating their own power, cities become less reliant on external energy. Yet, challenges exist, such as energy storage and efficiency during cloudy days. The technology is evolving, but there are still improvements to be made. As advancements continue, clean energy can become more accessible.
The chart below illustrates the benefits of solar energy compared to fossil fuels in terms of carbon emissions, job creation, and cost savings over a 10-year period. Solar energy systems provide a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, promote job growth in the clean energy sector, and result in substantial savings for consumers.
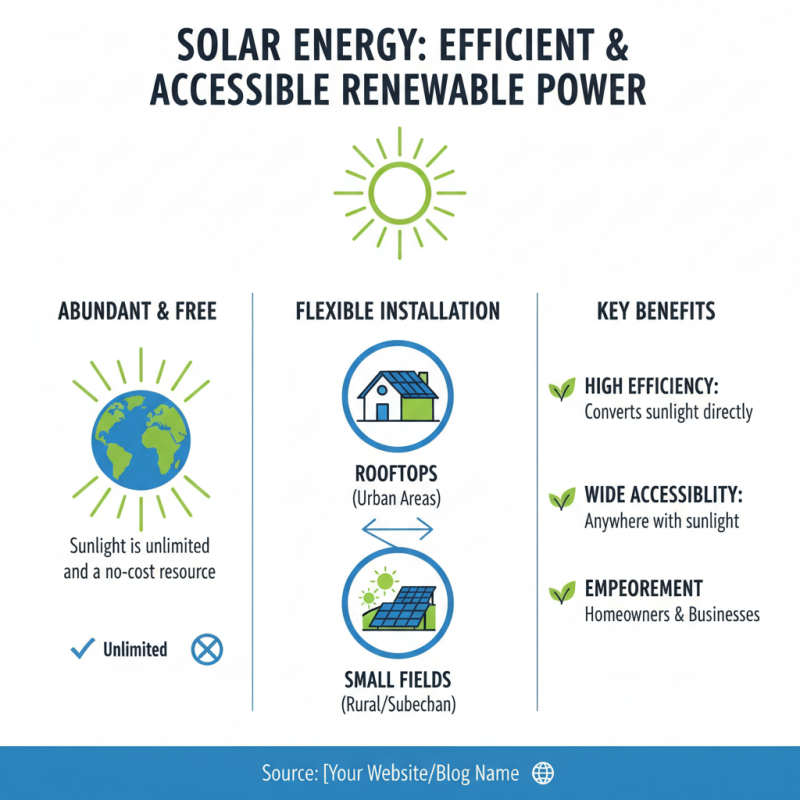
Solar energy stands out among renewable sources for its efficiency and accessibility. Sunlight is abundant and free. Unlike wind or hydro power, solar panels can be installed almost anywhere, from rooftops to small fields. This flexibility allows homeowners and businesses to harness energy even in urban areas.
However, solar energy systems have limitations. They depend heavily on sunlight, so cloudy days can reduce efficiency. Energy storage solutions, like batteries, can be expensive. This makes some potential users hesitant. In contrast, wind and hydro power can generate energy more consistently in certain regions. Yet, they require vast areas and face ecological concerns.
Ultimately, individuals must weigh these factors. Solar energy offers a path to reduced carbon footprints. But questions remain regarding cost, efficiency, and sustainability. Each choice deserves careful consideration. Making decisions about energy isn’t straightforward. It’s a balance of benefits and challenges.
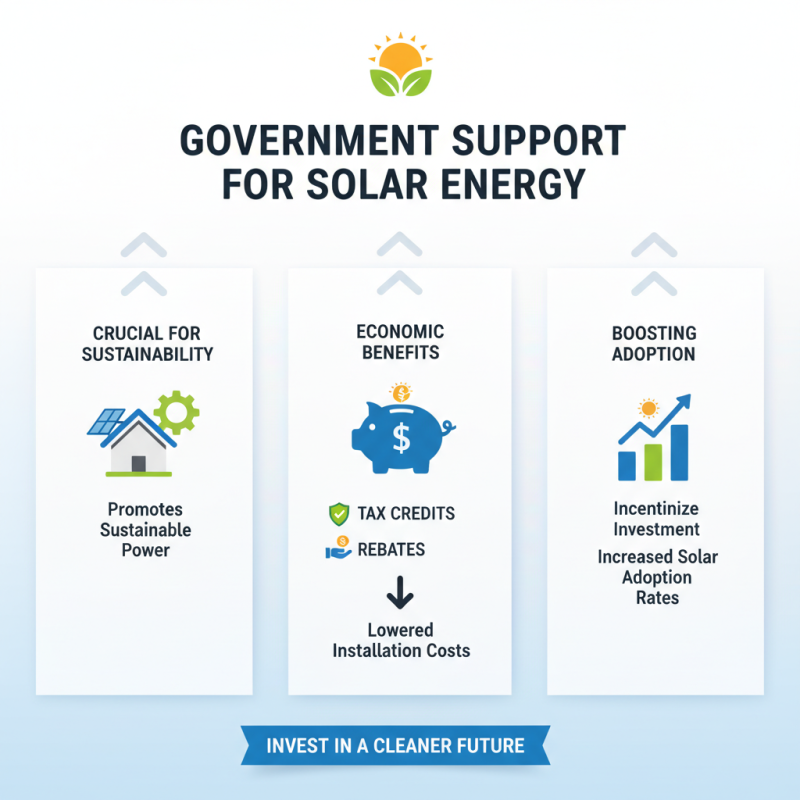
Government support for solar energy systems is crucial in promoting sustainable power. Incentives like tax credits and rebates encourage homeowners and businesses to invest. These economic benefits can significantly lower installation costs. A well-designed incentive program can bolster solar adoption rates.
Many states have introduced policies that facilitate solar energy growth. For instance, net metering allows individuals to earn credits for excess electricity generated. This not only saves money but also makes solar more appealing. However, disjointed regulations can create confusion. Some consumers worry about navigating various incentives.
The potential of solar power shines bright, yet challenges remain. Lack of awareness about available incentives hampers adoption efforts. More education is needed to inform the public. As government support evolves, we must reflect on how to enhance these programs for better accessibility.
Implementing solar power solutions presents various challenges and limitations.
One significant hurdle is the initial financial investment. While prices have decreased, the upfront costs can still be daunting.
Many households and businesses struggle to find funding or incentives to offset these costs. Additionally, the payback period can be lengthy, deterring some potential users.
Another challenge is energy storage. Solar power generation is intermittent.
This means that during cloudy days or at night, energy production drops.
High-quality batteries are needed to store that energy for later use, yet they can be expensive and may require regular maintenance.
This dependence on reliable battery technology raises concerns about overall efficiency.
Furthermore, not all locations are suitable for solar panels. Some regions have limited sunlight, reducing overall effectiveness.
This can lead to frustration for those who invest in solar energy, only to realize the output is less than expected.
These limitations remind us that while solar energy is a promising step toward sustainability, it requires careful consideration and planning.